Security Through Observability
Observability is great for understanding the ramifications of your system. In brief, massively distributed application stacks demand more sophisticated tools than traditional metrics/monitoring, because engineers must be able to ask new questions and get…

By: Andy Isaacson
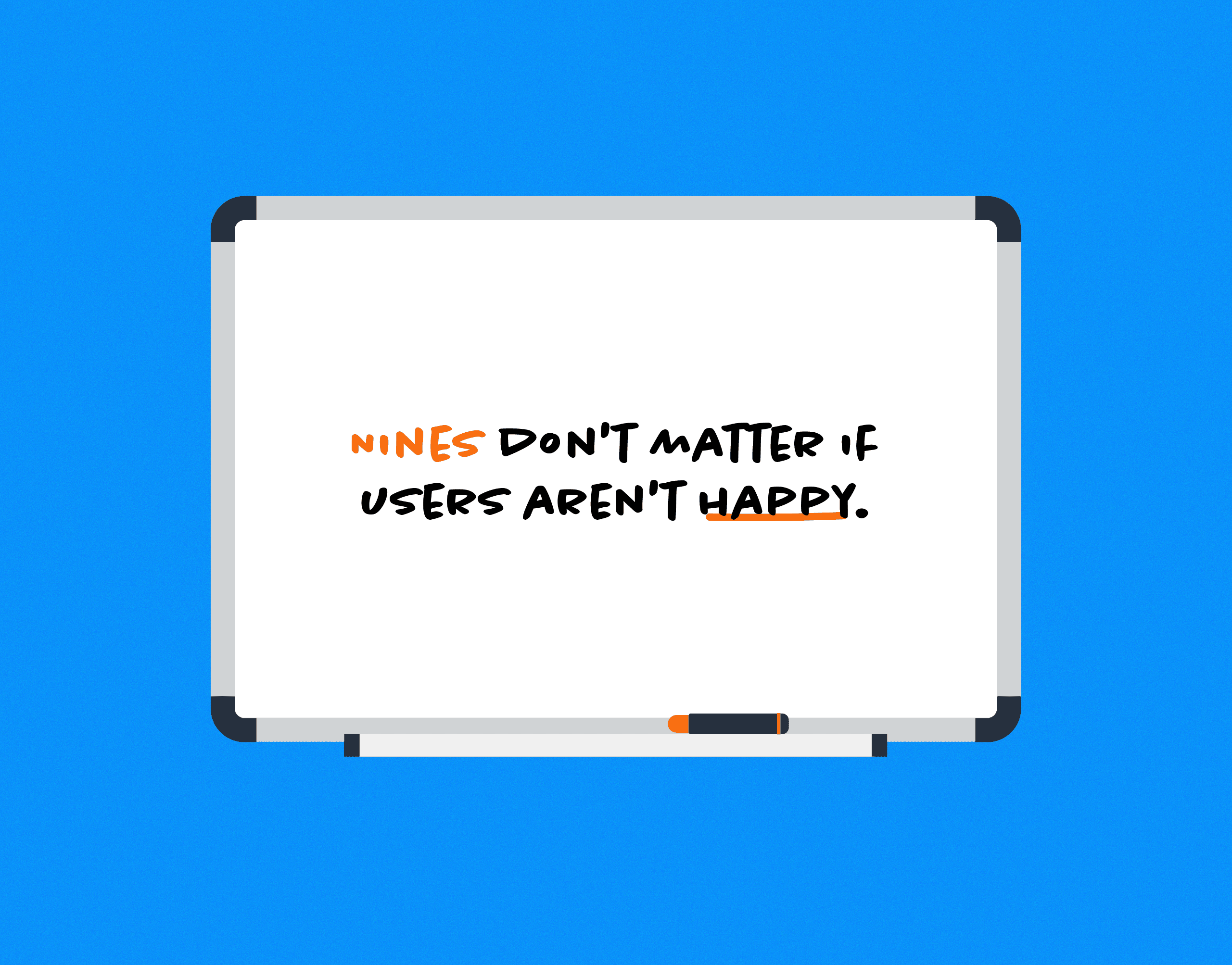
Observability is great for understanding the ramifications of your system. In brief, massively distributed application stacks demand more sophisticated tools than traditional metrics/monitoring, because engineers must be able to ask new questions and get new answers when the system surprises them. User happiness is the ultimate consequence of the systems we build, and as Charity is fond of saying (and as people are fond of quoting her):
"Nines don't matter if users aren't happy." Put this on your whiteboard. https://t.co/eMiyKxPEoZ
— John Arundel (@bitfield) October 19, 2017
Now, what happens when those ramifications potentially include the actions of malicious outsiders?
We make product security a core part of our software development practice here at Honeycomb; among other things this includes having a bug bounty program. (Hey, did I mention? Honeycomb has a bug bounty program!)
Any webapp bug bounty program is going to attract a certain amount of noise (or if we want to be charitable, “low-hanging fruit”); researchers trying PHP attacks on a Rails app, CSRF on a system using the Gorilla framework, SQL injection attempts on an app built on CouchDB.
I was curious about the occurrence of brute-force attacks on our login API endpoint after receiving a report that this API did not implement a rate limit. Since we use Honeycomb to observe Honeycomb, I queried our front-end app dataset with a breakdown by client IP for the login API:

The (several, it turns out) researcher’s brute-force trials easily stand out from normal usage levels. With two more clicks I turned this into a trigger that will email me the next time this pattern occurs.
As attacks evolve, so should your approach to noticing them
As we continue to gain experience with the regular patterns of life operating the Honeycomb service, that trigger will serve its purpose and eventually be retired for more sophisticated analysis.
Security response can never be just a checklist. Yes, of course you have to defend against the risks in the OWASP Top 10 list, and the low-hanging fruit of your bug-bounty’s $25 tier — but you can’t stop there. Threat actors mold their attacks to the observed behavior of the target system and unless your defenders can respond flexibly as well, you are going to lose. A system that is instrumented for observability lets defenders get real-time answers to track down active threats.
The sophistication of your high-cardinality triggers will evolve over time, and that’s a good thing! For example, my first trigger “alert when /login requests from a single IP exceeds 100/minute” wouldn’t catch a distributed attacker who sends only a few attempts per client IP.
High Cardinality threats
A recent morning paper post, “Tail attacks on web applications”, makes the point that attackers can manipulate the behavior of your system with malicious traffic that will never show up on your monitoring dashboard (the microbursts are too small to register) but their cumulative impact is queue congestion leading to application slowness and request failures. As our industry moves forward into a high-cardinality, observable future, we’ll learn together how to find these attacks using data.
Beyond augmenting your ability to debug issues that arise in your complex distributed systems, having real observability means you can inform your defenses with real data about how attackers interact with those systems.
Looking to see more of what’s going on in your environment? Sign up for a free trial!
Want to know more?
Talk to our team to arrange a custom demo or for help finding the right plan.